Angioedema, Definition, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications
 |
| Angioedema, Definition, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications |
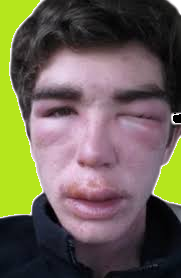
Angioedema is swelling that occurs under the skin. This condition is generally harmless. However, angioedema can occur in the throat and make it difficult to breathe. This condition is dangerous and must be treated immediately.
Angioedema is generally an allergic reaction, but some cases of angioedema are caused by inherited disorders. Sometimes, it is not known what causes this condition.
Angioedema causes generalized swelling in certain parts of the body. Some parts of the body that are more susceptible to angioedema are the eyelids, lips, and tongue.
Causes of Angioedema
The causes of angioedema are very diverse and can be grouped into four types, namely:
1. Allergic angioedema
This type of angioedema occurs due to allergic reactions, including:
- Food allergies, especially fish, nuts, shellfish, milk and eggs
- Drug allergies, such as certain types of antibiotics, aspirin, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Allergies due to insect bites
- Allergy due to pollen
- Allergy to latex, a type of rubber used in rubber gloves, balloons, or condoms
2. Drug-induced angioedema
A person can develop angioedema due to the use of certain drugs even though they do not have an allergy to these drugs. Swelling can occur shortly after taking the drug, but it can also appear months or years afterward.
Some types of drugs that can trigger angioedema are:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen
- ACE inhibitors for hypertension, eg ramipril, perindopril, and lisinopril
- ARB class hypertension drugs, including valsartan, losartan, and irbesartan
3. Hereditary angioedema
This type of angioedema runs in families. This condition is caused by a deficiency of the C1-esterase inhibitory protein in the blood. Lack of protein can trigger dilation of blood vessels and tissue swelling.
The emergence of symptoms of hereditary angioedema sometimes has no known trigger. However, in some people, the condition can be triggered by:
- Stress
- Surgical or dental procedures
- Use of birth control pills
- Pregnancy
- Injury or infection
4. Idiopathic angioedema
Idiopathic angioedema is angioedema with no known cause. Experts suspect this condition is related to disorders of the immune system.
Swelling in idiopathic angioedema can be triggered by the following conditions:
- • Stress or anxiety
- • Minor infection
- • Exercise that is too strenuous
- • Weather that is too hot or too cold
- • Medical conditions, such as lupus or lymphoma (very rare)
- • Gene changes, such as mastocytosis
Angioedema risk factors
Angioedema can happen to anyone. However, there are a number of factors that can increase a person's risk of developing this condition, including:
- Feeling stressed or restless
- Experiencing sudden changes in temperature
- Have had angioedema before
- Have a family history of angioedema
- Have allergies, for example to food or drugs
- Have asthma, hepatitis, lymphoma, lupus, HIV, thyroid disease, or Epstein-Barr virus infection
- Taking ACE inhibitors or ARB . drugs
- Ever received a blood transfusion
Symptoms of Angioedema
The main symptom of angioedema is swelling beneath the skin's surface due to fluid buildup in the deep layers of the skin. Generally, this condition occurs in the hands, feet, the area around the eyes, lips, tongue, and genitals. In severe cases, swelling occurs in the throat and intestines.
The swollen part of angioedema will enlarge, and feel thick and solid. Angioedema can also cause redness, pain, and a burning sensation in the skin. Usually, angioedema also occurs with urticaria or hives.
A number of other symptoms can also result from swelling. These symptoms include:
- Stomach ache
- Diarrhea
- Vomit
- Hard to breathe
- Dizziness and feeling like passing out
When to go to the doctor
Check with your doctor if you experience swelling of the skin or tongue for no apparent reason. If the swelling you experience is accompanied by symptoms of shortness of breath, dizziness, and you want to pass out, seek medical attention immediately to the ER. This condition can be an anaphylactic reaction that can be life-threatening.
Angioedema diagnosis
The doctor will ask you about the symptoms you are experiencing and what things might trigger the symptoms. The doctor will also ask about other diseases (including allergies) that the patient has and the medications he is currently taking. In addition, the doctor will also ask if any of the patient's family has experienced similar symptoms.
After that, the doctor will perform a physical examination, especially on the part of the body that is experiencing swelling. The doctor will also listen to the patient's breath sounds to detect if there is swelling in the throat.
Based on questions and answers, the doctor can suspect the cause of angioedema. From there, the doctor will perform additional tests to determine the cause.
If angioedema is suspected to be caused by allergies, the doctor will run allergy tests. Allergy testing can be done in two ways, namely:
• Skin prick test (skin prick)
The skin prick test is done by pricking the patient's skin using a tool that has been given a small amount of allergen (allergy-triggering substance), to see a mild allergic reaction on the patient's skin.
• Blood test
A sample of the patient's blood will be examined to see how the patient's immune system reacts to certain allergens.
If an allergy is not suspected, or if an allergy test is not positive, your doctor may be able to test your C1 esterase inhibitor protein level to determine hereditary angioedema.
Angioedema Treatment
Angioedema usually goes away on its own within a few days. However, there are several independent treatments that can be done to help relieve symptoms, namely:
- Cold compress the swollen area
- Wear loose clothing to prevent skin irritation
- Do not scratch the swollen area
- Shower with cold water
- Avoid foods that can trigger allergies
- Consult a doctor before using drugs, especially ACE inhibitors
If the self-medication above is not enough to relieve symptoms, people with angioedema are advised to consult a doctor. In general, swelling due to angioedema can be treated with antihistamine tablets or corticosteroid tablets.
However, in patients whose swelling is severe, doctors can give corticosteroid injections. Meanwhile, in anaphylactic reactions, administration of epinephrine injections should also be done to treat shock.
It should be noted that the above treatments may not be effective in patients with hereditary angioedema. In this condition, medications that can help relieve symptoms include:
- Ecallantide
- Icatibat
- C1 esterase . inhibitors
Complications of Angioedema
In some cases, angioedema can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Dehydration due to vomiting and diarrhea
- Total airway obstruction
- Asphyxia (lack of oxygen)
- Dead
Angioedema Prevention
Angioedema can be prevented by avoiding triggering factors, for example by avoiding foods, drugs, or other factors that can trigger this reaction, and managing stress well.
To help remember, you can note down anything that can trigger symptoms of angioedema. In addition, it is advisable to consult with your doctor before taking medication, especially if you or your family have a history of this disease.
In people with hereditary angioedema, doctors may prescribe oxandrolone or danazol to reduce the risk of recurrence of swelling. Another option is the administration of tranexamic acid, especially in female patients and children.
Related Search:
- angioedema,
- hereditary angioedema,
- what is angioedema,
- angioedema definition,
- angioedema lips,
- angioedema treatment,
- angioedema symptoms,
- idiopathic angioedema,
- angioedema pictures,
- angioedema icd 10,
- angioedema causes,
- ace inhibitor angioedema,
- lisinopril angioedema,
- foods to avoid with angioedema,
- define angioedema,
- angioedema tongue,
- what causes angioedema,
- icd 10 code for angioedema,
- angioedema of hands,
- hereditary angioedema treatment,
- angioedema hives,
- angioedema eyes,
- icd 10 angioedema,
- how to reduce angioedema swelling,
- urticaria angioedema,
- angioedema hands,
- angioedema face,
- angioedema with urticaria,
- hereditary angioedema symptoms,
- urticaria with angioedema,
- symptoms of hereditary angioedema,
- acquired angioedema,
- angioedema intestinal,
- vibratory angioedema,
- intestinal angioedema,
- treatment for angioedema of the lips,
- arb angioedema,
- angioedema allergy,
- losartan angioedema,
- bradykinin angioedema,
- angioedema rash,
- angioedema bradykinin,
- allergic angioedema,
- angioedema legs,
- angioedema anaphylaxis,
- how long does angioedema last,
- angioedema lisinopril,
- allergy angioedema,
- angioedema and urticaria,
- angioedema icd9,
- what is hereditary angioedema,
- angioedema in legs,
- angioedema leg,
- angioedema lip,
- angioedema on legs,
- angioedema vs anaphylaxis,
- chronic urticaria and angioedema,
- urticaria and angioedema,
- hereditary angioedema pictures,
- angioedema autoimmune,
- angioedema feet,
- type 3 hereditary angioedema,
- lip angioedema,
- angioedema treatment guidelines,
- tranexamic acid angioedema,
- hereditary angioedema type 3,
- autoimmune angioedema,
- hereditary angioedema hae,
- hae hereditary angioedema,
- chronic angioedema,
- facial angioedema,
- angioedema urticaria,
- uvular angioedema,
- angioedema from lisinopril,
- diagnosing hereditary angioedema,
- hives and angioedema,
- angioedema dog,
- types of angioedema,
- angioedema and hives,
- que es la angioedema,
- angioedema allergic reaction,
- amlodipine angioedema,
- icd 10 for angioedema,
- que es angioedema,
- angioedema in dogs,
- angioedema signs,
- uticaria angioedema,
- diagnosis of hereditary angioedema,
- angioedema of the throat,
- orolingual angioedema,
- acute angioedema,
- hereditary angioedema diagnosis,
- angioedema uvula,
- angioedema signs and symptoms,
- angioedema que es,
- signs of angioedema,
- angioedema throat,
- images of angioedema,
- angioedema images,
- bradykinin mediated angioedema,

Post a Comment for "Angioedema, Definition, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications"