Type 2 Diabetes, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications
Definition of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a disease that causes blood sugar levels to rise due to abnormalities in the body's ability to use the hormone insulin. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes.
Insulin is a hormone that helps blood sugar (glucose) enter the body's cells to be converted into energy. This hormone is produced by the pancreas when a person eats. In type 2 diabetes, high blood sugar levels occur due to insulin resistance, which is a cell condition when the body cannot use the insulin hormone properly.
 |
| Type 2 Diabetes, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications |
Worldwide, it is estimated that 1 in every 11 adults has diabetes. Of these, 90 percent of them suffer from type 2 diabetes. Apart from adults, type 2 diabetes can also affect children and adolescents.
Causes and Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body is unable to use insulin normally. There are several factors that can increase a person's risk of developing type 2 diabetes, namely:
- Genetic or hereditary factors
- Overweight or obesity
- Often consume foods and drinks that contain sugar and simple carbohydrates
- Lack of physical activity and exercise
- Certain conditions, such as high blood pressure or polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
Patients with type 2 diabetes can experience a variety of symptoms, such as sores that are difficult to heal, blurred vision, and numbness or tingling in the hands or feet. However, these symptoms take a long time to appear. In some cases, this condition may not even be noticed until complications occur.
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment and Prevention
Methods for dealing with type 2 diabetes include adopting a healthy lifestyle and diet, as well as administering medication or insulin. While still undergoing treatment, patients need to undergo blood sugar tests and routine health checks.
Type 2 diabetes can be prevented by adopting the following healthy lifestyle:
- Eat a complete and balanced nutritious diet
- Choose foods high in fiber, low in fat and low in calories
- Avoid consuming foods that are high in sugar and fat
- Exercising regularly
- Maintain ideal body weight
In addition to making some of the efforts above, patients who are at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes are also advised to undergo regular health checks.
Type 2 Diabetes Complications
Some of the complications that can be experienced by people with type 2 diabetes are:
- Heart disease
- Strokes
- Impaired vision (diabetic retinopathy)
- Kidney failure
- Diabetic wounds (diabetic ulcers)
- Alzheimer's disease
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes results from insulin resistance, which is when the body becomes immune or unresponsive to insulin. Insulin itself helps cells absorb and convert sugar into energy. Insulin resistance causes sugar to not enter the cells so that the sugar in the blood remains high.
These conditions make the pancreas have to work harder to produce insulin so that glucose can enter the cells. However, over time, pancreatic cells will be damaged due to overwork so that they cannot produce insulin. This causes glucose to build up in the blood.
It is not known exactly what causes insulin resistance. However, it is suspected that type 2 diabetes is triggered by a combination of the following factors:
- A genetic condition that affects the body's ability to produce insulin
- Being overweight or obese is at risk of causing insulin resistance in cells
- Metabolic syndrome, in the form of high blood sugar, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, high triglycerides, and waist circumference that exceeds normal
- Pancreatic damage, which results in disruption of the insulin production process
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
The risk of developing diabetes is higher in people who are 45 years of age or older. This risk can also occur in people whose immediate family has type 2 diabetes.
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes is higher in people who have the following conditions:
- Prediabetes
- Disorders of the heart and blood vessels
- Low HDL cholesterol levels
- Gestational diabetes, which is diabetes that occurs during pregnancy
- PCOS
Apart from being triggered by the conditions above, the following lifestyle can also increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes:
- Unhealthy eating patterns, such as frequent fast food and sugar-containing drinks
- Lack of exercise or physical activity
- Smoking habit
- Often stressed
- Lack of rest or lack of sleep
- Too much sleep
Although it generally occurs in adults, type 2 diabetes can also be experienced by children and adolescents, especially if they have the risk factors above. In addition, people are also more susceptible to this condition as they age.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Basically, the symptoms of type 2 diabetes are similar to those of type 1 diabetes. However, the appearance of the symptoms of type 2 diabetes tends to take longer. In some cases, type 2 diabetes does not even cause symptoms until complications occur.
The following are some of the symptoms that type 2 diabetes sufferers can experience:
- Easily thirsty
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Often feel hungry
- Weight loss
- The body feels tired
- Blurred vision
- Difficult to heal when injured
- Frequent infections
- Numbness or tingling in hands or feet
- Dry mouth
- Red, swollen and painful gums
- Some parts of the skin are black (akantosis nigrikans), usually the armpits and neck
When to See a Doctor
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes are often difficult to detect. Therefore, check blood sugar levels regularly, especially if you have risk factors for this disease. Through early examination and treatment, the risk of complications can be prevented.
Check with your doctor if you experience symptoms of type 2 diabetes, especially if accompanied by the following complaints:
- Breath smells like fruit
- Severe nausea and vomiting
- Severe stomach pain
- dazed
- Loss of consciousness
Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
To diagnose type 2 diabetes, the doctor will perform a series of blood sugar tests, including:
- HbA1c
The HbA1c test aims to check blood sugar levels in the last 2–3 months. The normal level of the HbA1c test is not more than 5.7%.
- Fasting blood sugar test
This test aims to check blood sugar levels in a fasting state. Before undergoing this test, the patient will be asked to fast for 8 hours.
- Blood sugar tolerance test
After undergoing a fasting blood sugar test, the patient will be asked to drink a special sugar solution and return to check blood sugar periodically within 2 hours.
- Current blood sugar test
This test aims to check blood sugar levels at random times.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will order at least two types of blood tests. If needed, the doctor will perform other tests to determine the type of diabetes you are experiencing, such as an antibody test.
Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
There are several methods that can be used to treat type 2 diabetes. The doctor will determine the right method and according to the patient's condition, including:
1. Diet and Exercise
Adopting a healthy lifestyle by exercising regularly and eating a balanced nutritious diet can not only reduce blood sugar levels, but can also reduce the risk of complications.
The doctor will advise the patient to eat foods that are rich in fiber and low in fat. If necessary, discuss with your doctor about the type of food that is good, as well as the right type and frequency of exercise. This is because the needs for food and exercise in each person can be different.
2. Drugs
Doctors can prescribe medications if lifestyle changes are not effective in lowering blood sugar levels. Some types of drugs that can be given are:
- Metformin, to reduce sugar production in the liver
- Glinide, such as nateglinide; and a sulfonylurea, such as glibenclamide or glipizide; to stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin
- Thiazolidinediones, such as pioglitazone, to stimulate the body's cells to be more sensitive to insulin
- DPP-4 inhibitors, such as linagliptin, sitagliptin, saxagliptin, or alogliptin, to increase insulin production and reduce sugar production by the liver
- GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as semaglutide, exenatide, or liraglutide, to slow the digestion of foods, especially those containing sugar, while lowering blood sugar levels
- SGLT2 inhibitors, such as dapagliflozin and empagliflozin, to encourage the kidneys to get rid of more sugar
It is important to remember, consulting a doctor is necessary before using the above drugs. This is so that the doctor adjusts the type and dosage of the drug to your condition so that the risk of side effects can be avoided.
If the drugs above are not effective, the doctor can give insulin injections. Insulin is available in several types, each of which works in a different way. Discuss with your doctor about the right type of insulin for you.
3. Bariatric surgery
Bariatric surgery is only recommended for overweight patients whose condition cannot be treated with diet and exercise. This procedure aims to change the shape of the digestive tract so that food portions can be limited and nutrients absorbed are reduced. That way, the weight will decrease.
Routine Blood Sugar and Health Screening
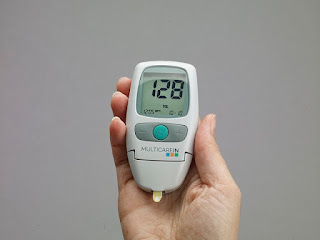
Diabetics are advised to routinely check their blood sugar levels independently using a blood sugar test kit. Consult with your doctor to find out when and how often this examination needs to be done.
In addition to an independent blood sugar test, periodic blood tests in the laboratory also need to be carried out to determine the success of the treatment. These blood tests include:
- HbA1c test
- Urine test
- Cholesterol level check
- Liver and kidney function tests
The doctor will also carry out periodic eye examinations to detect damage to the optic nerve, as well as examination of the feet to see if there is any disturbance or damage to the nerves in the legs. Patients are also advised to routinely undergo cardiac examinations.
Type 2 Diabetes Complications
Some of the complications that type 2 diabetes patients can experience include:
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels, such as heart attacks and strokes
- Nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy), which can be characterized by numbness or pain in the legs, or disturbances in sexual function
- Chronic and severe kidney damage (diabetic nephropathy) that can lead to kidney failure
- Eye damage (diabetic retinopathy) which is at risk of causing vision problems
- Disorders of the skin, such as bacterial infections, viral infections, or wounds that are difficult to heal
- Hearing disorders
- Sleep apnea
- Alzheimer's disease
In addition to the conditions above, type 2 diabetes can also cause complications in the form of diabetic ketoacidosis, which can result in coma and death.
Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes can be reduced by adopting a healthy lifestyle. In addition to reducing risk, living a healthy lifestyle can also prevent complications of type 2 diabetes.
Some of the efforts that can be made include:
- Meet nutritional needs with balanced nutritious foods, but choose foods that are high in fiber, low in fat, and low in calories.
- Avoid drinks and foods that are high in sugar and fat.
- Do 30 minutes of exercise every day, for example, morning walk, cycling, or swimming.
- Lose weight if you are overweight.
- Maintain ideal body weight according to body mass index (BMI).
- Avoid sitting too long by getting up every 30 minutes and walking for a few minutes.
- Avoid smoking habits.
- Manage stress well, and get enough sleep.
- Do regular health checks.
Related Searches:
- type 2 diabetes symptom,
- type 2 diabetes symptoms,
- what is type 2 diabetes,
- type 1 vs type 2 diabetes,
- symptoms of type 2 diabetes,
- difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes diet,
- type 2 diabetes treatment,
- type 2 diabetes mellitus,
- signs of type 2 diabetes,
- what causes type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes medications,
- can type 2 diabetes be reversed,
- type 2 diabetes vs type 1,
- type 2 diabetes icd 10,
- can you reverse type 2 diabetes,
- what is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes food list,
- type 1 and type 2 diabetes,
- is type 2 diabetes genetic,
- whats the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes,
- is type 2 diabetes reversible,
- what's the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes,
- causes of type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes with insulin,
- pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes,
- what's the difference between type1 and type 2 diabetes,
- a1c chart for type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes can be cured,
- can type 2 diabetes be cured,
- snacks type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes cure,
- type 2 diabetes diet plan printable,
- icd 10 code for type 2 diabetes,
- reversing type 2 diabetes,
- how to reverse type 2 diabetes,
- icd 10 type 2 diabetes,
- how to prevent type 2 diabetes,
- diet for type 2 diabetes,
- foods to avoid with type 2 diabetes,
- can you get rid of type 2 diabetes,
- new pill for type 2 diabetes,
- treatment for type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes treatments,
- how do you get type 2 diabetes,
- symptoms of type 2 diabetes in women,
- type 2 diabetes cause,
- type 2 diabetes diabetic diet,
- type 2 diabetes insulin,
- type 2 diabetes foods to avoid,
- risk factors for type 2 diabetes,
- reverse type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes causes,
- type 2 diabetes diet sheet pdf,
- type 2 diabetes symptoms in adults,
- type 2 diabetes definition,
- type 2 diabetes food chart,
- best time to check blood sugar type 2 diabetes,
- cause of type 2 diabetes,
- best diet for type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes diet sheet,
- type 2 diabetes risk factors,
- type 2 diabetes blood sugar levels,
- type 2 diabetes meal plan,
- early signs of type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes diagnosis,
- a1c levels for type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes weight loss,
- is type 2 diabetes an autoimmune disease,
- how to cure type 2 diabetes permanently,
- nursing diagnosis type 2 diabetes,
- how to treat type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes medication,
- insulin pump for type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes low blood sugar symptoms,
- type 2 diabetes prevention,
- difference between type1 and type 2 diabetes,
- can you cure type 2 diabetes,
- does type 2 diabetes require insulin,
- signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications,
- which is worse type 1 or type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes bracelet,
- symptoms type 2 diabetes,
- medication for type 2 diabetes,
- difference in type 1 and type 2 diabetes,
- can type 2 diabetes go away,
- what is difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes,
- which of the following helps prevent type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes complications,
- is type 2 diabetes worse than type 1,
- type 2 diabetes life expectancy,
- treatment of type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes recipes,
- drugs for type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes diet plan,
- dka in type 2 diabetes,
- how to get rid of type 2 diabetes,
- type 2 diabetes test,

Post a Comment for "Type 2 Diabetes, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications"